The technical solution of the present invention will be described in detail and exemplified with the following accompanying drawings to illustrate its workflow.
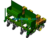
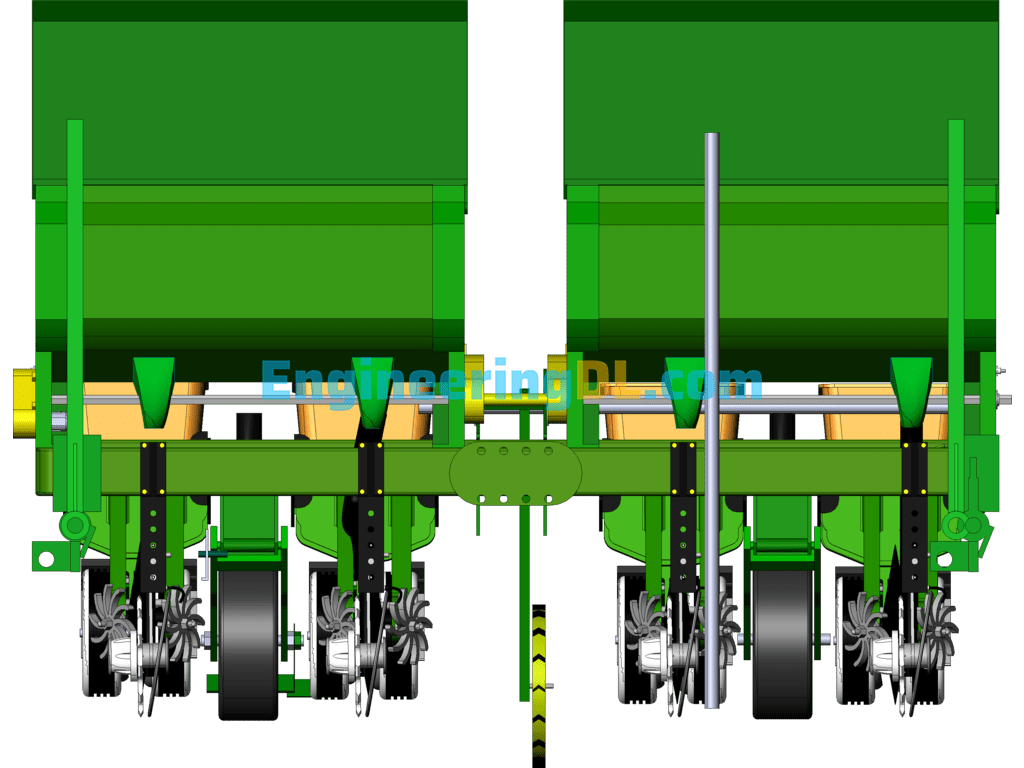
Figure 1 shows the front view of the corn precision sowing variable fertilizer machine; it contains 1, sowing quality controller 2 fertilizer box, 3 fertilizer device, 5 sowing mulching wheel, 6 sowing drive ground wheel 7 sowing and fertilizer machine frame and 8 rower. The fertilizer box 2 is located above and below the sowing and fertilizer machine frame 7 connected to the fertilizer application device 3 where the rower 8 is connected to the sowing and fertilizer machine frame 7; each fertilizer box 2 is equipped with a material level detection sensor 12 for the implementation of the detection of the state of the material in the box; the sowing quality controller 1 is installed in the front of the fertilizer box.
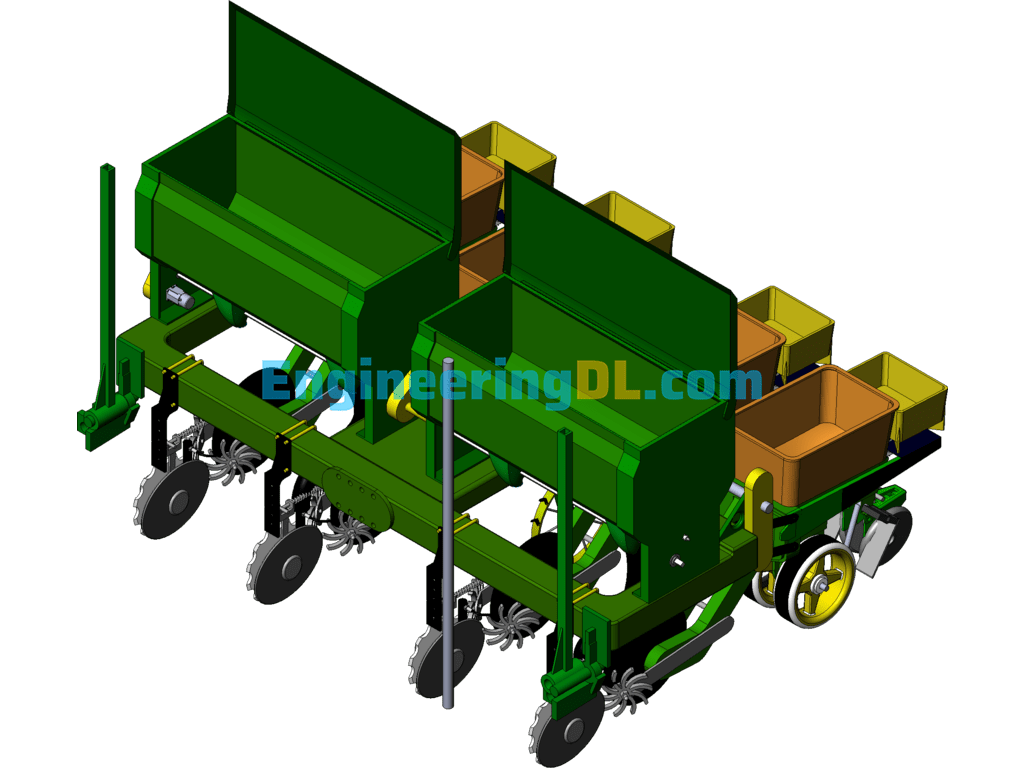
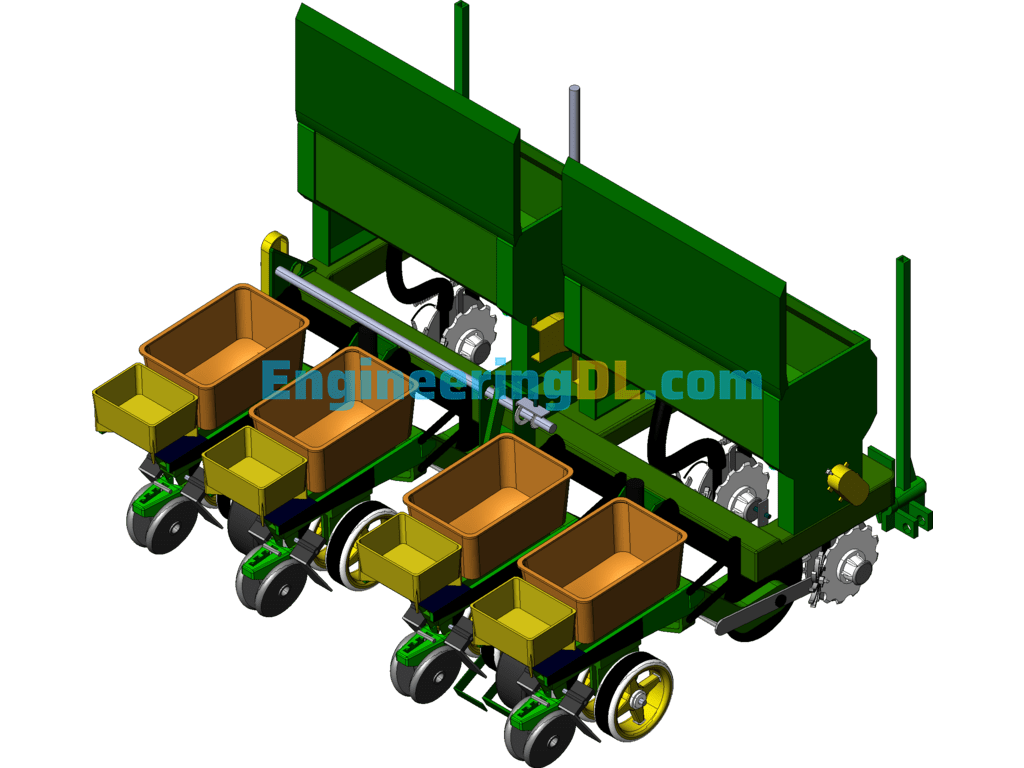
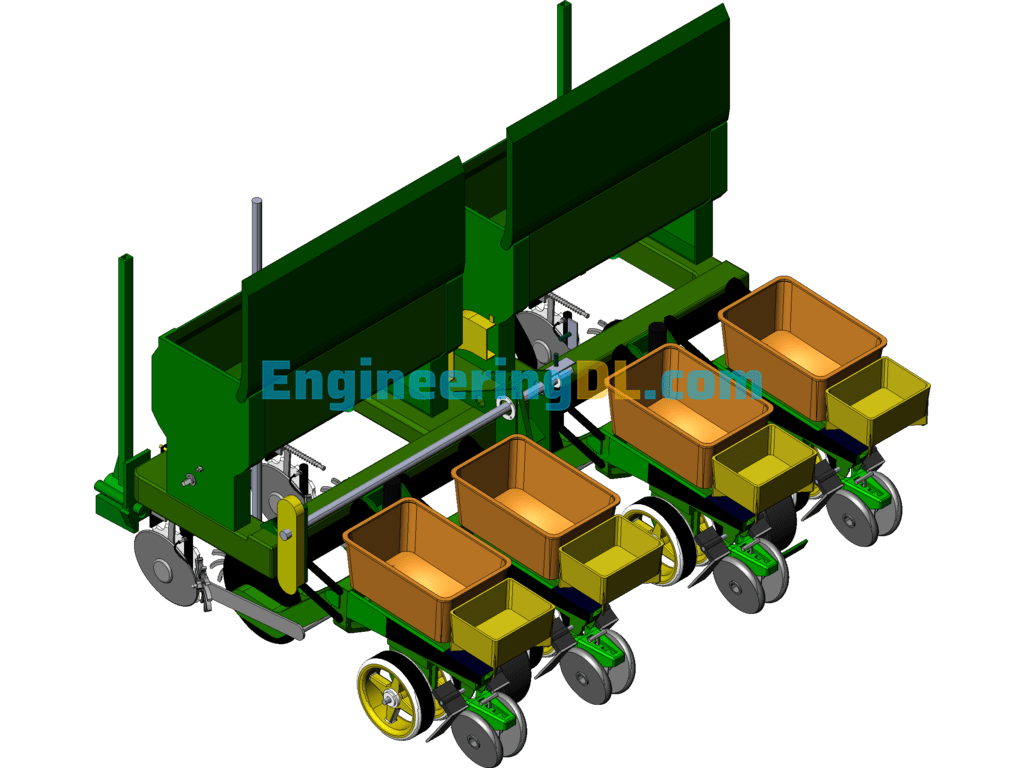
Further reference to Fig. 2 and Fig. 3 to illustrate the relative positions; Fig. 2 and Fig. 3 contain 9 grass divider assembly 10 fertilizer opener 11 servo drive motor 12 material level monitoring sensor and 13 seeding box 14 fertilizer box 15 fertilizer mulching wheel 16 seeding mechanism assembly; where the seeding drive ground wheel 6 is located in the middle of the seeding and fertilizer machine frame 7, and four fertilizer opener 10 below the frame in a symmetrical The four grass divider assembly 9 is located behind each fertilizer trencher 10 and connected to the fertilizer seeding machine frame 7; the rear end of the frame is connected to the seeding mechanism assembly 16 and fertilizer replenishment mechanism in turn. Its Omron proximity speed switch 18 and capacitive fertilizer clogging sensor 23 are mounted with reference to Figures IV and V. The fertilizer application vehicle terminal 21 and seeding vehicle terminal 22 are located at the front end of the tractor cockpit as shown in Figure VI, and are connected to the controller on the seeder through the CAN bus protocol.
Implementation method of precision seeding control.
A photoelectric sensor is installed at the side wall of the seed discharge tube in the sowing mechanism assembly to detect the implementation sowing status; meanwhile, the Omron proximity speed switch 18 implements the detection of the implementation speed of the drive shaft speed gear 20; the measurement signals of both are transmitted to the sowing quality controller 1 for analysis, and the theoretical sowing status is analyzed by the Omron proximity speed switch 18 and the actual sowing status is analyzed by the photoelectric sensor signal. After comparing and analyzing the two, the result of sowing is whether there is sowing leakage and the amount of sowing leakage combined with the vehicle GPS system can record the location of the sowing leakage in real time and transmit the work information to the sowing vehicle terminal 21 through CAN bus protocol to generate relevant technical documents to store and display the sowing status; it is convenient for the subsequent intelligent sowing leakage and replenishment operation to realize the control of precision sowing; at the same time, the sowing box 14 is equipped with the material level sensor to monitor the seed state in real time. At the same time, the sowing box 14 is equipped with material level sensors, which can monitor the status of the seed in real time and transmit it to the vehicle seeding terminal 22 for display, providing the driver with early warning of lack of seed.
Variable fertilizer application control method.
The invention uses a corn no-till fertilizer planter, which needs to go through two fertilization processes when planting; one is deep fertilization and the other is surface fertilization. When fertilizer application is carried out, each fertilizer tube 22 has a capacitive fertilizer blockage sensor 23 installed on the side wall to detect the blockage of fertilizer and the actual fertilizer application rate. If the blockage or the fertilizer application rate does not match the set rate, the alarm will be alerted on the fertilizer application vehicle terminal 21; in addition, the fertilizer application quality controller 4 is used to drive and control the speed of the servo motor 11 to control the fertilizer application rate to meet the fertilizer application rate requirements. Each fertilizer application box 3 and replenishment box 15 is equipped with a level monitoring sensor 12 to detect the amount of fertilizer and to provide fertilizer warning. The amount of fertilizer required by the land is determined by combining the GPS module in the fertilizer application vehicle terminal 22 to obtain the latitude and longitude information and the machine operating speed. The fertilizer application quality control system in the terminal generates fertilizer application decisions based on each sensor information collected by the data acquisition module and sends them to the fertilizer application quality controller 4 in real time to achieve precise fertilization of the machine at the current position. Operating parameters such as operating speed, latitude and longitude information, current fertilizer application volume, current discharging volume and blockage are displayed in real time through the fertilizer application vehicle terminal; in this way, the control of variable fertilization is realized.
(At the time of writing the invention patent designed by myself, a school student, I hope to help to friends in need)
Specification: Precision Variable Seeder Corn No-Till Fertilizer Seeder SolidWorks, 3D Exported
|
User Reviews
Be the first to review “Precision Variable Seeder Corn No-Till Fertilizer Seeder SolidWorks, 3D Exported”
You must be logged in to post a review.




There are no reviews yet.